Proven Strategies to Lose 10kg Fast: Your Complete Guide to Effective Weight Loss, Diet, and Exercise

Javaburn Coffee: Unveiling Weight Loss with Java Burn
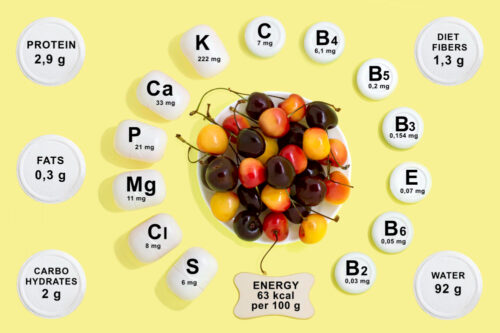
The Complete Guide to ABCDEK Vitamins: Everything You Need to Know for Optimal Health
In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining a well-balanced diet is critical for long-term health and vitality. While we often hear about the importance of eating healthy, many of us struggle to understand what “eating healthy” really means, especially when it comes to essential vitamins. Among the most important nutrients we need daily are the ABCDEK vitamins—a group of vitamins that work together to support everything from your immune system to bone strength.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into each of the ABCDEK vitamins—how they benefit your body, where to find them in your diet, and what happens when you don’t get enough.
Chapter 1: What are ABCDEK Vitamins?
The ABCDEK vitamins are a collective term for Vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K, all of which are essential for your body to function optimally. These vitamins are crucial for various bodily functions, including boosting immunity, improving skin health, strengthening bones, and helping your body heal and repair itself.
Vitamins can be divided into two main categories:
- Water-soluble vitamins (Vitamins B and C): These vitamins dissolve in water and are excreted through urine, meaning you need a continuous daily supply from your diet.
- Fat-soluble vitamins (Vitamins A, D, E, and K): These are absorbed along with fats and are stored in your body, meaning they can be consumed less frequently.
Each vitamin has a unique role in your overall health, and they are all important for specific bodily functions. Let’s dive into each vitamin individually to explore how they can contribute to your well-being.
Chapter 2: Vitamin A – The Visionary Nutrient
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin known for its role in maintaining healthy vision, skin health, and immune function. It’s commonly found in two forms:
- Retinol (preformed vitamin A) from animal sources such as liver, eggs, and dairy.
- Beta-carotene (provitamin A) from plant sources like carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach.
Health Benefits of Vitamin A
- Supports Vision: Vitamin A helps maintain the health of the cornea, retina, and epithelial tissues. It’s especially vital for night vision.
- Boosts Immunity: Vitamin A is essential for the immune system, helping to fight infections by promoting white blood cell production.
- Promotes Skin Health: This vitamin is necessary for the maintenance and repair of skin cells. It’s often used in acne treatments and skincare products.
Signs of Vitamin A Deficiency
A deficiency in Vitamin A can lead to night blindness, dry eyes, and skin issues. In severe cases, it can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
How to Get More Vitamin A
- Animal Sources: Liver, dairy products, eggs.
- Plant Sources: Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, and cantaloupe.
Recommended Daily Intake
- Men: 900 micrograms
- Women: 700 micrograms
Chapter 3: Vitamin B Complex – The Energy Boosters
The Vitamin B complex consists of eight essential vitamins that play a crucial role in converting food into energy. These include:
- B1 (Thiamine)
- B2 (Riboflavin)
- B3 (Niacin)
- B5 (Pantothenic acid)
- B6 (Pyridoxine)
- B7 (Biotin)
- B9 (Folate)
- B12 (Cobalamin)
Health Benefits of Vitamin B Complex
- Energy Production: B vitamins help convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into usable energy.
- Brain Function: B6, B9 (folate), and B12 are particularly important for brain health and cognitive function.
- Cell Metabolism: These vitamins help in the formation of red blood cells and other cellular functions.
- Heart Health: Folate and B12 play an important role in reducing homocysteine levels, a factor in heart disease risk.
Signs of Vitamin B Deficiency
Symptoms of Vitamin B deficiency vary but often include fatigue, poor concentration, anemia, and nerve damage. Deficiency in B12 or folate can lead to serious conditions like pernicious anemia.
How to Get More Vitamin B
- Animal Sources: Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
- Plant Sources: Leafy greens, beans, peas, nuts, and seeds.
Recommended Daily Intake
- Varies by B vitamin. For example, adults need about 2.4 micrograms of Vitamin B12 daily.
Chapter 4: Vitamin C – The Immune Booster
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin and a powerful antioxidant. It’s best known for its role in strengthening the immune system and aiding in skin health and collagen production.
Health Benefits of Vitamin C
- Boosts Immunity: Vitamin C enhances the immune system by stimulating the production of white blood cells and protecting them from harmful substances.
- Promotes Healthy Skin: It is essential for the production of collagen, a protein that supports skin, cartilage, and bones.
- Enhances Iron Absorption: Vitamin C improves the absorption of iron from plant-based foods, reducing the risk of anemia.
- Antioxidant Power: Its antioxidant properties help combat oxidative stress, which can contribute to chronic diseases.
Signs of Vitamin C Deficiency
A lack of Vitamin C can lead to scurvy, which causes symptoms like gum disease, bruising, and weakened immune function. Inadequate Vitamin C intake may also result in dry skin, slow healing of wounds, and fatigue.
How to Get More Vitamin C
- Fruits: Oranges, strawberries, kiwi, and grapefruit.
- Vegetables: Bell peppers, broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts.
Recommended Daily Intake
- Men: 90 milligrams
- Women: 75 milligrams

Chapter 5: Vitamin D – The Sunshine Vitamin
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that your body produces when exposed to sunlight. It plays a critical role in calcium absorption, promoting bone health, and supporting immune function.
Health Benefits of Vitamin D
- Strengthens Bones: Vitamin D helps regulate calcium and phosphate levels in the body, ensuring strong bones and teeth.
- Supports Immune Function: Adequate levels of Vitamin D have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Promotes Mood Stability: Some studies suggest that Vitamin D can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
A lack of Vitamin D can lead to osteoporosis in adults and rickets in children, both of which cause weak and fragile bones. Deficiency may also contribute to chronic fatigue, muscle pain, and depression.
How to Get More Vitamin D
- Sunlight: Your body produces Vitamin D when exposed to the sun.
- Food Sources: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), fortified milk, and egg yolks.
Recommended Daily Intake
- Adults: 600 IU (International Units), though some experts recommend higher doses for certain populations.
Chapter 6: Vitamin E – The Antioxidant Defender
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that helps protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals. It is important for maintaining healthy skin, eyes, and a strong immune system.
Health Benefits of Vitamin E
- Protects Cells: Vitamin E defends your cells against oxidative damage caused by free radicals, which are linked to aging and many diseases.
- Improves Skin Health: Vitamin E is commonly used in skincare products for its ability to nourish and protect the skin.
- Supports Immune Function: It enhances the body’s ability to fend off infections by boosting immune cell function.
Signs of Vitamin E Deficiency
Vitamin E deficiency is rare, but it can lead to muscle weakness, vision problems, and immune system issues. People with malabsorption disorders may be more at risk.
How to Get More Vitamin E
- Food Sources: Nuts (almonds, hazelnuts), seeds, vegetable oils, and green leafy vegetables.
Recommended Daily Intake
- Adults: 15 milligrams
Chapter 7: Vitamin K – The Bone Builder
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for blood clotting and bone health. It activates proteins that help your blood coagulate and prevent excessive bleeding.
Health Benefits of Vitamin K
- Aids Blood Clotting: Vitamin K is necessary for the production of proteins that allow blood to clot properly.
- Supports Bone Health: It helps regulate calcium levels in the body, contributing to strong bones and reducing the risk of fractures.
- May Prevent Heart Disease: Some studies suggest thatVitamin K aids in the proper clotting of blood and plays a key role in bone health. It helps to regulate calcium levels in your body, ensuring that calcium is directed to your bones rather than building up in your arteries. This vitamin is essential for preventing osteoporosis and supporting cardiovascular health. Vitamin K deficiency can lead to excessive bleeding and weakened bones.
How to Get More Vitamin K
- Food Sources: Leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, and Brussels sprouts.
Recommended Daily Intake
- Adults: 120 micrograms for men, 90 micrograms for women.
Chapter 8: How to Maintain an Adequate Intake of ABCDEK Vitamins
The best way to ensure you’re getting enough ABCDEK vitamins is to consume a well-balanced diet filled with a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Here’s how you can optimize your vitamin intake:
- Incorporate Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits like oranges, strawberries, and vegetables such as spinach, kale, and bell peppers are rich in vitamins A, C, E, and K.
- Include Protein-Rich Foods: Meat, poultry, and fish are great sources of vitamin B complex and Vitamin D.
- Use Healthy Fats: Vitamin A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble, so include healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil in your diet.
- Sunlight Exposure: Spend time outdoors for natural Vitamin D production from sunlight.
- Consider Supplements: If you have trouble getting enough vitamins from food, consider taking high-quality supplements, but always consult with a healthcare provider.
Chapter 9: Signs You Might Need More ABCDEK Vitamins
While a balanced diet is the best way to obtain necessary vitamins, there are times when you might need additional supplementation. Here are some signs you might not be getting enough ABCDEK vitamins:
- Fatigue and lack of energy could indicate a deficiency in B vitamins, which are responsible for energy production.
- Poor immune function or frequent infections might signal low Vitamin C or Vitamin A levels.
- Bone pain and muscle weakness can be signs of Vitamin D deficiency.
- Dry skin or skin conditions like eczema might indicate you need more Vitamin E.
- Excessive bleeding or easy bruising may mean you’re not getting enough Vitamin K, which is vital for proper blood clotting.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it might be worth evaluating your diet or consulting a healthcare provider for advice.
Chapter 10: The Role of ABCDEK Vitamins in Disease Prevention
These vitamins don’t just keep you feeling good day-to-day; they also play critical roles in preventing long-term health problems. Here’s how:
- Heart Disease: Vitamins B6, B12, C, and E all contribute to cardiovascular health by reducing homocysteine levels and oxidative stress, which can lead to heart disease.
- Osteoporosis: Vitamin D and Vitamin K are crucial for bone density and calcium absorption, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Cancer: Vitamins A, C, and E, being powerful antioxidants, help protect cells from damage that can lead to cancer.
- Eye Health: Vitamin A and Vitamin E protect against conditions like cataracts and macular degeneration.
Regular consumption of these vitamins through a nutrient-dense diet can help stave off chronic diseases and promote longevity.
Chapter 11: The Future of ABCDEK Vitamins
With advances in nutritional science, the importance of vitamins continues to grow. Scientists are continually discovering how micronutrients like the ABCDEK vitamins influence not only physical health but also mental well-being and aging processes. Here are a few trends on the horizon:
- Personalized Nutrition: As research into genetics and nutrition advances, we are moving toward personalized dietary recommendations. Certain populations may require higher levels of specific vitamins based on genetic predisposition or lifestyle.
- Fortification of Foods: Many countries are increasing the fortification of foods with vitamins like D and B12 to combat widespread deficiencies.
- Supplements and Enhanced Foods: While supplements are already widely used, food producers are creating enhanced products that contain additional vitamins for better health outcomes. We are seeing more fortified drinks, snacks, and meal replacements designed to meet specific vitamin needs.
As our understanding of the role of vitamins grows, so will the potential to use these essential nutrients in new and innovative ways to improve overall health and quality of life.
Chapter 12: Final Thoughts on ABCDEK Vitamins
The ABCDEK vitamins are not just individual nutrients; they form a comprehensive team that helps your body function at its best. From your skin and eyes to your immune system and bones, these vitamins support countless vital processes.
To ensure you are getting enough of each vitamin, it’s essential to focus on a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods. If you have dietary restrictions or health conditions that prevent you from getting adequate nutrients, supplements can also be an excellent option—but always consult a healthcare provider first.
By taking care to include all of these important vitamins in your daily routine, you will be well on your way to achieving optimal health.